If you've ever experienced stomach pain after coughing, you're not alone. Many people wonder why their stomach hurts when they cough, and this discomfort can be both confusing and concerning. While occasional stomach pain from coughing is usually harmless, persistent or severe pain may indicate an underlying issue that requires medical attention.
Coughing is a natural reflex that helps clear irritants from your respiratory system. However, when it becomes persistent, it can put significant strain on your abdominal muscles and surrounding tissues, leading to discomfort in the stomach area. Understanding why this happens and how to manage it is crucial for maintaining your overall health.
In this article, we will explore the reasons behind stomach pain from coughing, its causes, and the best ways to alleviate it. Whether you're dealing with a minor annoyance or a more serious condition, this guide will provide you with the information you need to address your concerns effectively.
Read also:Mt Charleston Weather By Month Your Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Relationship Between Coughing and Stomach Pain
- Common Causes of Stomach Pain from Coughing
- Muscle Strain and Its Role
- Diagnosing the Underlying Cause
- Managing Stomach Pain from Coughing
- Effective Home Remedies
- Medical Treatment Options
- Preventing Stomach Pain from Coughing
- When to See a Doctor
- Conclusion
Understanding the Relationship Between Coughing and Stomach Pain
Coughing is an essential mechanism your body uses to protect itself from foreign particles, mucus, or irritants. However, prolonged or forceful coughing can strain various parts of your body, including your stomach muscles. This strain can lead to discomfort or pain in the abdominal area, which is why many people ask, "Why does my stomach hurt from coughing?"
When you cough, your diaphragm and abdominal muscles contract forcefully to expel air from your lungs. Repeated or intense coughing can cause these muscles to become overworked, leading to soreness or even minor injuries. Additionally, the pressure created during coughing can affect other structures in your abdomen, such as your stomach lining or intestines, contributing to the pain.
How Coughing Affects Your Abdominal Muscles
Your abdominal muscles play a critical role in supporting your core and aiding in various bodily functions, including breathing and coughing. During a coughing episode, these muscles contract to help expel air from your lungs. If the coughing is severe or prolonged, the muscles can become fatigued or strained, leading to pain or discomfort in your stomach area.
Common Causes of Stomach Pain from Coughing
There are several reasons why your stomach may hurt after coughing. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for determining the appropriate treatment. Below are some of the most common causes:
- Intense Coughing Fits: Forceful or prolonged coughing can strain your abdominal muscles, leading to soreness or pain.
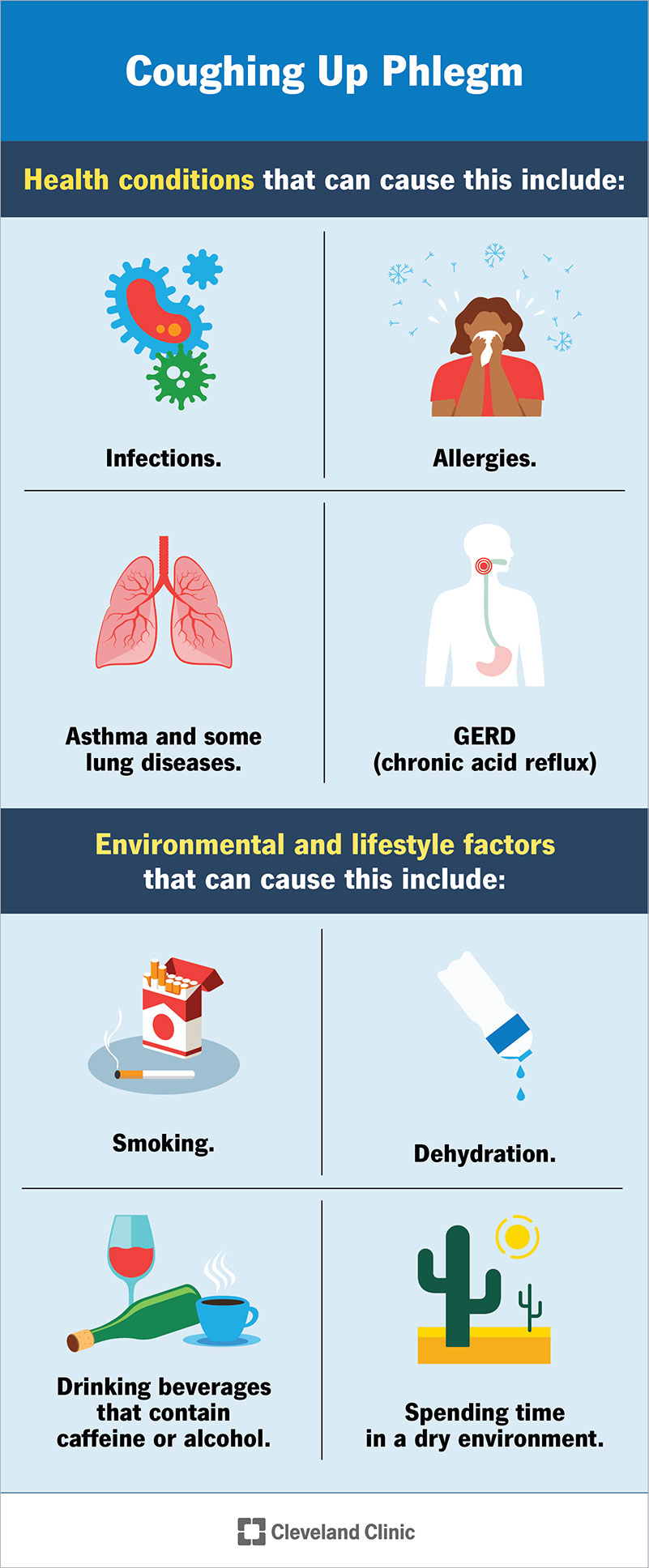
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Coughing can exacerbate GERD symptoms, causing stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus and leading to abdominal discomfort.
- Hiatal Hernia: A hiatal hernia occurs when part of your stomach pushes through the diaphragm, potentially causing pain during coughing episodes.
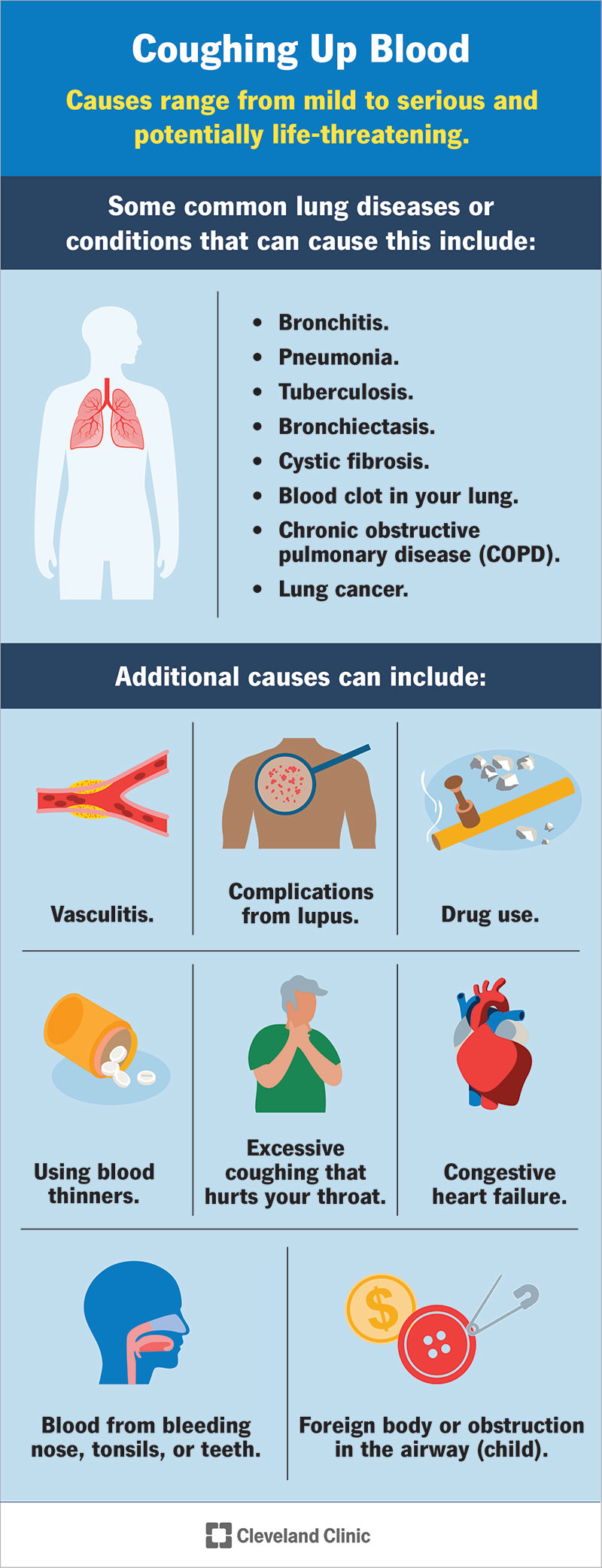
- Infections: Respiratory infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, can cause persistent coughing, which may lead to stomach pain.
- Allergies or Asthma: These conditions can trigger chronic coughing, putting additional strain on your abdominal muscles.
Other Possible Causes
Besides the above, other factors may contribute to stomach pain from coughing, such as:
- Abdominal hernias
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Pancreatitis
- Gallbladder issues
Muscle Strain and Its Role
Muscle strain is one of the most common reasons why your stomach hurts from coughing. When you cough forcefully, your abdominal muscles contract repeatedly, which can lead to small tears or inflammation in the muscle fibers. This strain is often accompanied by soreness or tenderness in the affected area.
Read also:How To Email Shein A Comprehensive Guide To Contacting Shein Successfully
Signs of Muscle Strain
If you suspect that your stomach pain is due to muscle strain, look out for the following symptoms:
- Persistent soreness in the abdominal area
- Tenderness when pressing on the muscles
- Difficulty moving or stretching the muscles
- Mild swelling or bruising in the area
Diagnosing the Underlying Cause
While muscle strain is a common cause of stomach pain from coughing, it's essential to rule out more serious conditions. If your pain persists or worsens, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. They may perform the following diagnostic tests:
- Physical examination to assess muscle strain or hernias
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, to check for structural issues
- Endoscopy to evaluate the esophagus and stomach lining
- Blood tests to check for infections or inflammatory markers
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild stomach pain from coughing is usually not a cause for concern, certain symptoms may indicate a more serious issue. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe or worsening pain
- Fever or chills
- Vomiting or nausea
- Difficulty breathing
- Blood in your stool or vomit
Managing Stomach Pain from Coughing
Managing stomach pain from coughing involves addressing both the underlying cause of the cough and the resulting muscle strain. Here are some strategies to help alleviate your discomfort:
Rest and Recovery
Give your abdominal muscles time to heal by avoiding activities that strain them further. Resting and applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help relieve muscle pain and reduce inflammation. However, always follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if needed.
Effective Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can help alleviate stomach pain from coughing. Try the following:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Use a humidifier to soothe your airways and reduce coughing
- Apply a warm compress to your stomach to relax tense muscles
- Practice deep breathing exercises to strengthen your diaphragm
Natural Cough Suppressants
Some natural remedies can help reduce coughing and minimize stomach pain:
- Honey and lemon tea
- Ginger tea
- Peppermint oil
Medical Treatment Options
If home remedies and over-the-counter treatments are ineffective, your healthcare provider may recommend additional medical interventions. These may include:
- Prescription medications to treat underlying conditions
- Physical therapy to strengthen your abdominal muscles
- Procedures to address structural issues, such as hernias
Addressing Chronic Cough
If your cough persists, identifying and treating the underlying cause is essential. Conditions such as asthma, GERD, or chronic bronchitis may require specific medical management to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Preventing Stomach Pain from Coughing
Preventing stomach pain from coughing involves addressing the root cause of the cough and taking steps to protect your abdominal muscles. Here are some tips:
- Stay hydrated to keep your airways moist and reduce coughing
- Avoid irritants, such as smoke or strong odors, that can trigger coughing
- Exercise regularly to strengthen your core muscles
- Practice good posture to reduce strain on your abdominal muscles
When to See a Doctor
If your stomach pain from coughing persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Stomach pain from coughing is a common issue that can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strain, GERD, or underlying medical conditions. By understanding the reasons behind this discomfort and taking appropriate steps to manage it, you can alleviate your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information. If you have any questions or concerns, feel free to leave a comment below or consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Stay informed and take control of your health today!