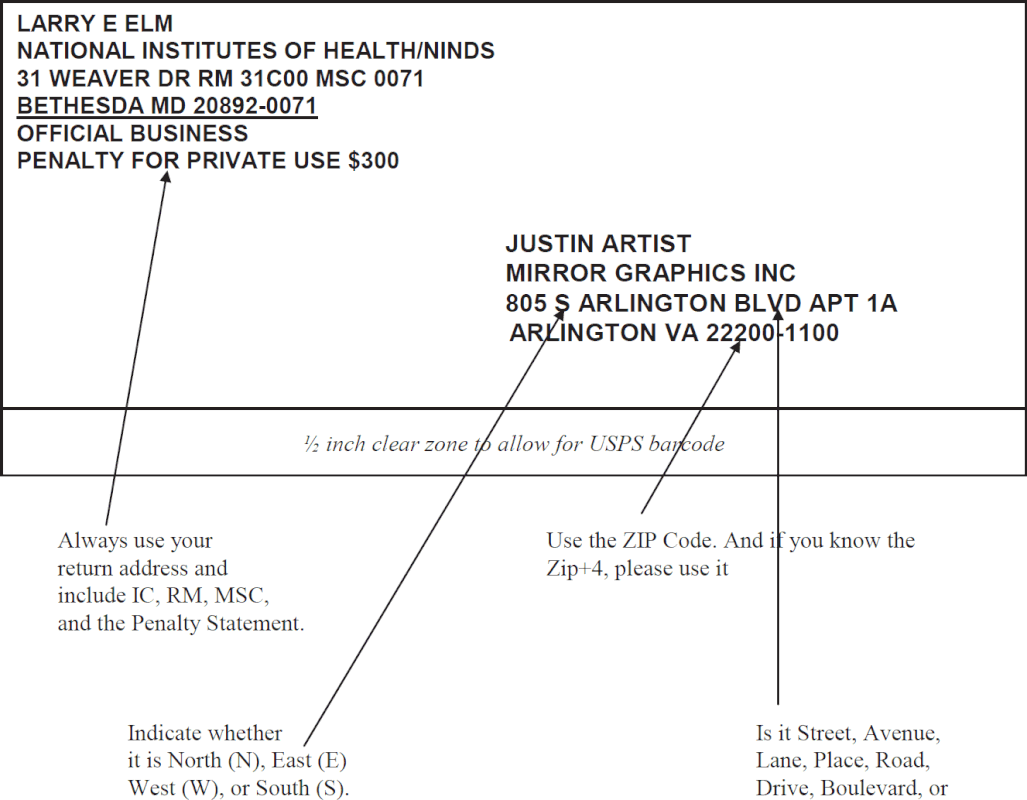
The US Postal Service is an example of a government-operated organization responsible for delivering mail and packages across the United States. Established in 1775, it has become an integral part of American infrastructure and daily life. As one of the oldest federal institutions, its role in connecting people and businesses has evolved significantly over the years.
From delivering handwritten letters to handling billions of e-commerce packages annually, the US Postal Service continues to adapt to modern demands. Its vast network spans across all 50 states, ensuring that every corner of the country remains connected regardless of geography or population density.
This article explores the significance of the US Postal Service, its historical context, and how it exemplifies a government service that plays a critical role in society. Whether you're interested in understanding its operational structure or learning about its challenges in the digital age, this guide will provide valuable insights.
Read also:New Action Movies In Hindi A Thrilling Journey Into The World Of Bollywood Action
Table of Contents
- The History of the US Postal Service
- Organizational Structure
- Services Offered by USPS
- Economic and Social Impact
- Challenges Faced by USPS
- Innovations in Postal Delivery
- Why USPS is an Example of Government Efficiency
- USPS Statistics and Key Figures
- Comparison with Private Delivery Services
- The Future of USPS
The History of the US Postal Service
The US Postal Service traces its roots back to 1775 when Benjamin Franklin was appointed as the first Postmaster General. Since then, it has grown into a massive organization serving millions of customers daily. Over the years, USPS has undergone numerous transformations, adapting to technological advancements and societal changes.
In the early days, mail delivery relied heavily on horse-drawn carriages and steamships. However, with the advent of automobiles, airplanes, and digital technologies, the postal service has embraced new methods to improve efficiency and speed. Today, USPS operates one of the largest vehicle fleets in the world, delivering mail to approximately 160 million addresses.
Key Milestones in USPS History
- 1775: Appointment of Benjamin Franklin as Postmaster General
- 1847: Introduction of adhesive postage stamps
- 1918: Launch of airmail service
- 1970: Establishment of the modern USPS under the Postal Reorganization Act
Organizational Structure
The US Postal Service operates as an independent agency of the federal government, responsible for managing all aspects of mail delivery and logistics. Its organizational structure is designed to ensure efficiency and accountability at every level. USPS employs over 600,000 workers, making it one of the largest employers in the United States.
At the helm of the organization is the Board of Governors, which oversees strategic decisions and policies. Below the board, various departments handle specific functions such as operations, finance, and customer service. This hierarchical structure enables USPS to maintain consistency and quality across its vast network.
Key Departments within USPS
- Operations: Responsible for mail processing and delivery
- Finance: Manages budgeting and financial planning
- Customer Service: Ensures satisfaction and resolves issues
Services Offered by USPS
The US Postal Service offers a wide range of services catering to individual and business needs. From standard mail delivery to specialized services like Priority Mail and Express Mail, USPS provides options for every type of shipment. Additionally, it offers financial services such as money orders and international mailing solutions.
One of the standout features of USPS is its commitment to universal service. Unlike private carriers, USPS delivers to every address in the country, regardless of profitability. This ensures that even remote and rural areas receive consistent service.
Read also:Civil Coffee Highland Park Your Ultimate Coffee Destination
Popular USPS Services
- First-Class Mail: For letters and small packages
- Priority Mail: For faster delivery of larger items
- Express Mail: Guaranteed overnight delivery
Economic and Social Impact
The US Postal Service plays a crucial role in the American economy and society. By connecting businesses and consumers, it facilitates commerce and supports job creation. In addition, USPS provides essential services to rural communities, ensuring they have access to mail and packages.
Socially, USPS serves as a lifeline for many individuals, especially seniors and those in underserved areas. It delivers medications, government benefits, and important documents, making it an indispensable part of daily life for millions of Americans.
Economic Contributions of USPS
- Supports over 1 million jobs indirectly
- Contributes billions of dollars to the national economy
- Facilitates e-commerce growth through package delivery
Challenges Faced by USPS
Despite its importance, the US Postal Service faces numerous challenges in the modern era. The rise of digital communication and e-commerce has disrupted traditional mail delivery, leading to declining revenue from letter mail. Additionally, the organization grapples with financial constraints and aging infrastructure.
To address these challenges, USPS must innovate and adapt to changing market conditions. This includes exploring new revenue streams, improving operational efficiency, and investing in technology to enhance customer experience.
Major Challenges for USPS
- Declining revenue from traditional mail
- Financial deficits and budget constraints
- Competition from private delivery services
Innovations in Postal Delivery
In response to evolving demands, the US Postal Service has implemented several innovative solutions to improve its operations. These include the use of automation, data analytics, and renewable energy technologies. By embracing innovation, USPS aims to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and provide better service to its customers.
One notable example is the deployment of automated sorting machines, which significantly speeds up mail processing. Additionally, USPS has invested in electric vehicles and solar-powered facilities to reduce its carbon footprint.
Examples of USPS Innovations
- Automated sorting systems
- Electric delivery vehicles
- Solar-powered postal facilities
Why USPS is an Example of Government Efficiency
The US Postal Service exemplifies how a government agency can deliver essential services efficiently and effectively. Despite its size and complexity, USPS maintains a high level of reliability and customer satisfaction. Its commitment to universal service and innovation sets it apart from private competitors.
Moreover, USPS operates without taxpayer funding, relying solely on revenue from its services. This demonstrates its ability to function as a self-sustaining entity while fulfilling its public mission.
Characteristics of USPS Efficiency
- Universal service coverage
- High reliability and consistency
- Self-sustaining financial model
USPS Statistics and Key Figures
Data and statistics provide valuable insights into the scale and impact of the US Postal Service. According to recent figures, USPS delivers approximately 48% of the world's mail volume, making it the largest postal service globally. Below are some key statistics that highlight its significance:
- Delivers to over 160 million addresses daily
- Operates a fleet of over 200,000 vehicles
- Processes and delivers billions of packages annually
Comparison with Private Delivery Services
While private delivery services like FedEx and UPS offer competitive alternatives, the US Postal Service remains unique in its mission and scope. Unlike these companies, USPS is committed to serving all addresses, regardless of profitability. This universal service obligation ensures equitable access to mail and package delivery for everyone.
Additionally, USPS often collaborates with private carriers, providing last-mile delivery services and leveraging its extensive network to enhance efficiency.
Key Differences Between USPS and Private Carriers
- Universal service obligation
- Non-profit organizational structure
- Focus on public service
The Future of USPS
Looking ahead, the US Postal Service is poised to continue evolving in response to changing demands. With advancements in technology and shifting consumer preferences, USPS must remain agile and innovative to thrive in the digital age. This includes exploring new business models, investing in cutting-edge technologies, and enhancing customer experience.
Furthermore, addressing financial challenges and modernizing infrastructure will be critical to ensuring the long-term sustainability of USPS. By prioritizing innovation and efficiency, the organization can continue to serve as a vital link in American society.
Conclusion
The US Postal Service is an example of a government-operated organization that plays a vital role in connecting people and businesses across the United States. From its rich history to its modern innovations, USPS exemplifies efficiency, reliability, and commitment to public service. Despite facing challenges in the digital age, it continues to adapt and evolve to meet the needs of its customers.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with USPS in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into topics related to logistics, technology, and public services. Together, let's celebrate the importance of USPS in our daily lives!