Living in Hawaii is a dream for many, but it comes with a unique set of financial considerations. The cost of living in Hawaii is significantly higher compared to most states in the U.S., making it essential to understand the expenses involved before relocating or planning a long-term stay. This article will delve into the various aspects of living costs, from housing and groceries to healthcare and transportation, providing you with a clear picture of what to expect.
Hawaii’s stunning landscapes, vibrant culture, and warm climate attract millions of visitors annually. However, the allure of paradise comes at a price. Understanding the financial implications of residing in Hawaii is crucial for anyone considering a move to the Aloha State.
In this guide, we will explore the cost of living in Hawaii in detail, offering insights into the economic realities of life on the islands. Whether you're planning a relocation, retirement, or simply curious about the expenses, this article will provide valuable information to help you make informed decisions.
Read also:Madden Nfl 24 Release Date Ps5 Everything You Need To Know
Table of Contents
- Overview of the Cost of Living in Hawaii
- Housing Costs in Hawaii
- Grocery Expenses
- Transportation Costs
- Healthcare Expenses
- Utilities and Bills
- Education Costs
- Entertainment and Leisure
- Taxes in Hawaii
- Tips for Managing the Cost of Living
Overview of the Cost of Living in Hawaii
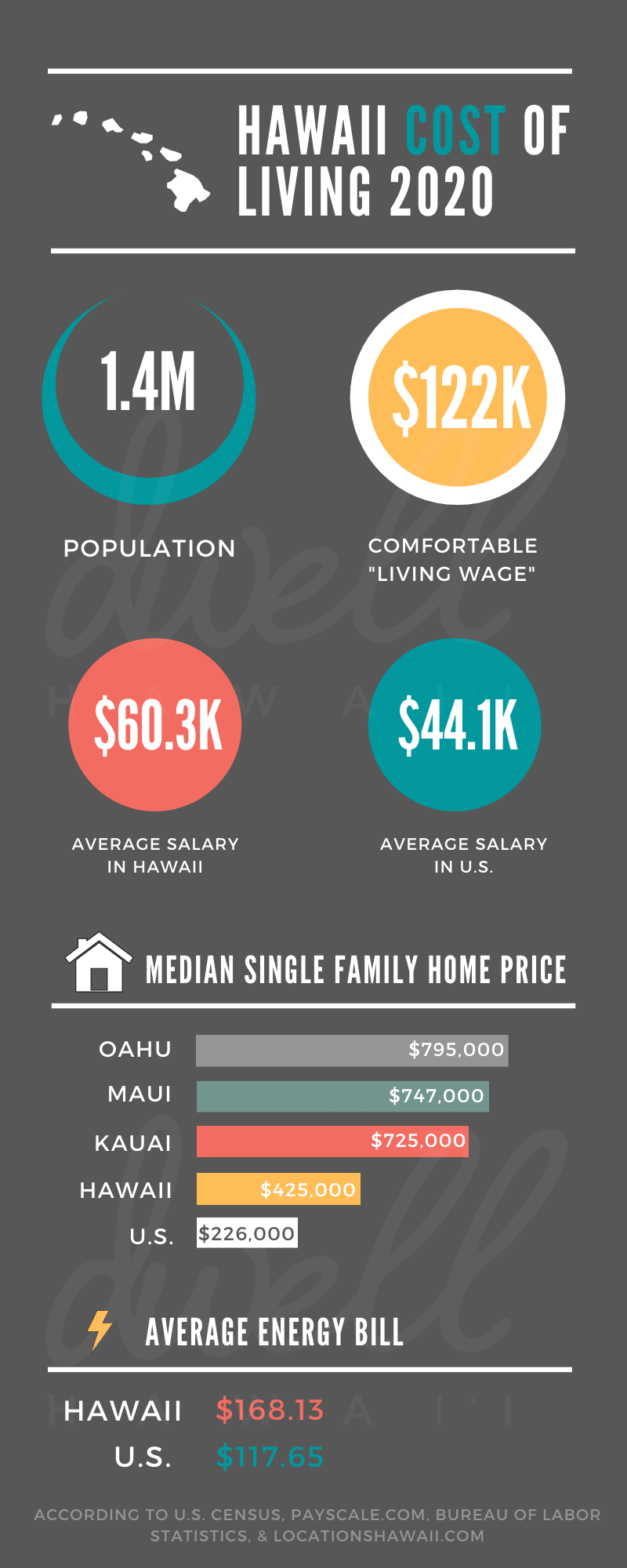
Hawaii is renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty and laid-back lifestyle, but it also ranks among the most expensive states in the U.S. The cost of living in Hawaii is influenced by several factors, including its remote location, limited land availability, and reliance on imports. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the overall cost of living in Hawaii is approximately 50% higher than the national average.
Key contributors to the high cost of living include housing, groceries, and transportation. While wages in Hawaii tend to be higher than in other states, they often fail to keep pace with the rising expenses. This section will provide a broad overview of the financial landscape in Hawaii, setting the stage for more detailed discussions in subsequent sections.
Housing Costs in Hawaii
Real Estate Prices
Housing is one of the most significant expenses in Hawaii, with real estate prices consistently ranking among the highest in the nation. The median home price in Hawaii exceeds $800,000, with prices varying significantly depending on the island and location. For example, Oahu, the most populated island, has some of the priciest neighborhoods, while areas like Kauai and Molokai offer more affordable options.
Key factors driving high housing costs include:
- Limited land availability due to conservation efforts and geographic constraints.
- High demand from both residents and tourists.
- Strict zoning laws that restrict development.
Rental Prices
Rentals in Hawaii are equally expensive, with the average monthly rent for a one-bedroom apartment ranging from $1,800 to $2,500. Honolulu, the state capital, is particularly costly, with some areas commanding rents of over $3,000 per month. Renters should also consider additional costs such as utilities, property taxes, and renters' insurance when budgeting for housing.
Grocery Expenses
Groceries in Hawaii are notably more expensive than in mainland U.S. states due to the state's reliance on imports. Fresh produce, dairy, and meat products often come from the mainland, adding to transportation and storage costs. On average, grocery expenses in Hawaii are 30-40% higher than the national average.
Read also:Delaware County Title Office A Comprehensive Guide To Property Transactions
To manage grocery costs, residents often rely on:
- Local farmers' markets for fresh, affordable produce.
- Bulk purchasing at wholesale clubs like Costco.
- Growing their own fruits and vegetables.
Transportation Costs
Public Transit
Public transportation in Hawaii is limited compared to larger cities on the mainland. The primary public transit system, TheBus, serves Oahu but has limited routes and hours. Residents often rely on personal vehicles for commuting, which adds to transportation costs.
Car Ownership
Car ownership in Hawaii comes with several expenses, including:
- Higher car insurance rates due to the state's no-fault insurance system.
- Increased fuel costs, as gasoline is imported and subject to state taxes.
- Maintenance and repair expenses, exacerbated by the state's humid climate.
Healthcare Expenses
Healthcare in Hawaii is generally more affordable than in other states, thanks to the state's unique healthcare system. The Hawaii Prepaid Health Care Act mandates that employers provide health insurance coverage for employees working over 20 hours per week. This has resulted in higher insurance coverage rates and lower out-of-pocket expenses for residents.
However, residents should still consider:
- Co-pays and deductibles for medical services.
- Prescription drug costs.
- Specialty care expenses, which may require travel to the mainland.
Utilities and Bills
Utilities in Hawaii are another significant expense, with electricity costs being among the highest in the nation. The state's reliance on imported fossil fuels contributes to this issue. Residents can expect to pay around $200-$300 per month for electricity, depending on usage and location.
Other utility costs include:
- Water and sewage services.
- Internet and cable packages.
- Trash collection and recycling fees.
Education Costs
Public Schools
Hawaii's public school system is funded by the state, making it one of the few states with a single school district. While tuition is free for public schools, parents may incur additional costs for school supplies, uniforms, and extracurricular activities.
Private Schools
Private schools in Hawaii offer diverse educational options but come with substantial tuition fees. Annual tuition can range from $8,000 to over $20,000, depending on the institution and grade level. Scholarships and financial aid are available to help offset these costs.
Entertainment and Leisure
Hawaii offers a wealth of entertainment and leisure activities, many of which are free or low-cost. Residents can enjoy beaches, hiking trails, cultural events, and community festivals without breaking the bank. However, certain activities, such as water sports and guided tours, can be expensive.
Cost-saving tips for entertainment include:
- Taking advantage of free or discounted admission days at museums and attractions.
- Joining local clubs or groups for social activities.
- Exploring natural attractions like parks and beaches.
Taxes in Hawaii
Taxes in Hawaii differ from those in other states, with a unique General Excise Tax (GET) replacing the traditional sales tax. The GET applies to most goods and services, ranging from 4% to 4.712% depending on the county. Additionally, residents pay state income taxes, property taxes, and fuel taxes.
Key tax considerations include:
- GET is included in the price of most goods and services.
- Property taxes vary by county and property type.
- State income tax rates are progressive, with higher rates for higher incomes.
Tips for Managing the Cost of Living
Living in Hawaii can be expensive, but there are strategies to help manage costs effectively:
- Budget carefully and track expenses to identify areas for savings.
- Explore local resources for affordable groceries, healthcare, and education.
- Take advantage of free or low-cost entertainment options.
- Consider living in less expensive areas or sharing housing costs with roommates.
Conclusion
The cost of living in Hawaii presents both challenges and opportunities. While expenses are higher than in most states, the quality of life and unique cultural experiences make it a desirable place to live for many. By understanding the financial realities and adopting cost-saving strategies, residents can enjoy the best of what Hawaii has to offer.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more insights into living in Hawaii and beyond. Mahalo for reading!