Cats are fascinating creatures, and understanding their pregnancy cycle is crucial for any cat owner or enthusiast. Whether you're a new breeder or simply curious about feline reproduction, this guide will provide you with all the essential information about the pregnancy cycle of cats. From the initial stages to postpartum care, we’ll cover everything you need to know.
Understanding the feline pregnancy cycle ensures that your cat receives the best possible care during this delicate period. This knowledge helps you recognize the signs of pregnancy, prepare for delivery, and support your cat throughout the process. Proper care during this time is vital for the health of both the mother and her kittens.
In this article, we’ll explore the various stages of the pregnancy cycle of cats, common challenges, and how to ensure a smooth journey for your feline friend. Let’s dive in and discover the intricacies of this natural and miraculous process.
Read also:Frontier Airline Flight Status A Comprehensive Guide To Stay Updated
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Pregnancy Cycle of Cats
- Stages of Cat Pregnancy
- Signs of Pregnancy in Cats
- Nutritional Needs During Pregnancy
- Common Health Issues During Pregnancy
- Preparing for Labor and Delivery
- Labor and Delivery Process
- Postpartum Care for Mother and Kittens
- Importance of Spaying Cats
- Conclusion
Introduction to the Pregnancy Cycle of Cats
The pregnancy cycle of cats, also known as gestation, is a remarkable biological process. On average, the gestation period lasts about 63 to 67 days, but this can vary slightly depending on the breed and individual cat. During this time, the queen (female cat) undergoes significant physical and hormonal changes.
The pregnancy cycle begins when the queen is successfully mated with a tomcat (male cat). After fertilization, the embryos travel to the uterus, where they implant and begin developing. Understanding this cycle is essential for providing appropriate care and support to ensure a healthy pregnancy and successful delivery.
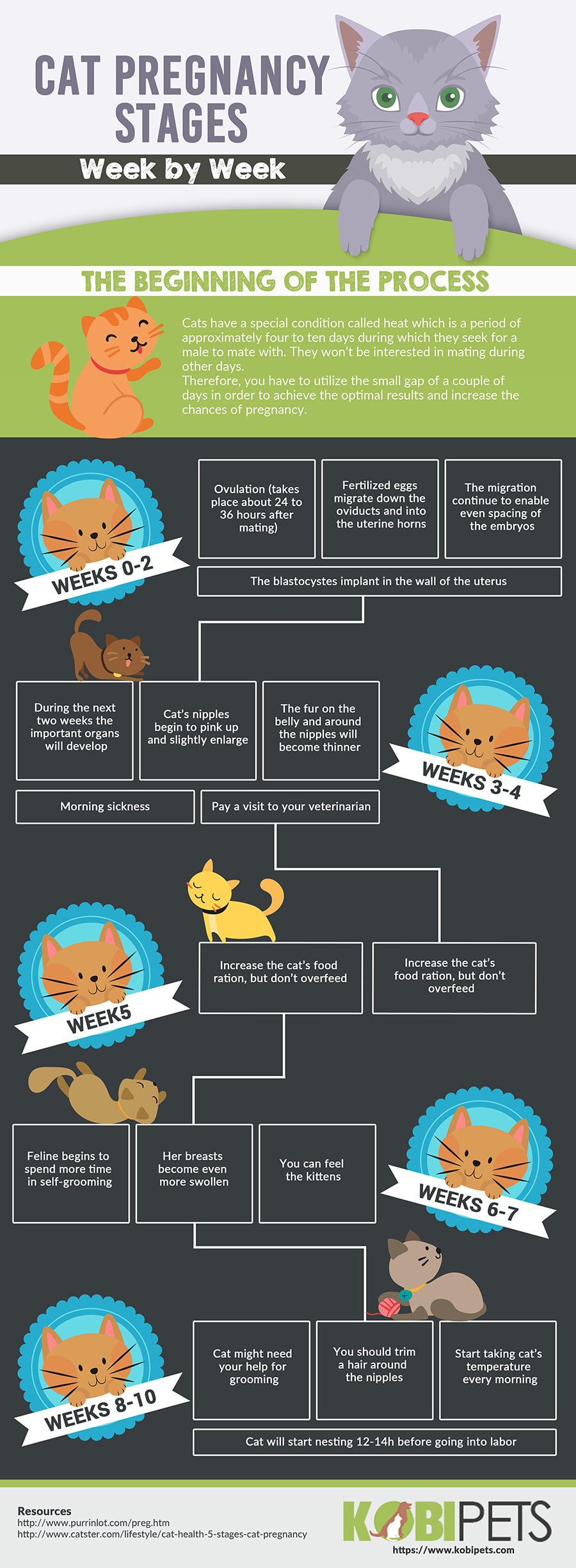
Stages of Cat Pregnancy
Week 1-2: Early Pregnancy
In the first two weeks, the embryos are implanting into the uterine lining. During this stage, there are usually no visible signs of pregnancy. However, the queen may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased affection or irritability.
Week 3-4: Fetal Development
By the third week, the embryos have developed into fetuses. At this stage, a veterinarian can confirm pregnancy through an ultrasound. The queen may start gaining weight, and her nipples may become more prominent and pink, a condition known as "pinking up."
Week 5-6: Rapid Growth
During weeks five and six, the kittens experience rapid growth. The queen’s abdomen will begin to enlarge, and she may start eating more to meet the increased nutritional demands. It’s crucial to provide a high-quality diet rich in protein and essential nutrients.
Week 7-9: Final Stages
In the final weeks, the kittens are fully developed and ready for birth. The queen may exhibit nesting behavior, seeking a quiet and comfortable place to give birth. She may also become more restless and may stop eating a day or two before labor begins.
Read also:Amc Theatres Merchants Crossing 16 Your Ultimate Guide To Entertainment
Signs of Pregnancy in Cats
Recognizing the signs of pregnancy in cats is essential for proper care. Here are some common indicators:
- Increased Appetite: The queen may eat more as her nutritional needs increase.
- Behavioral Changes: She may become more affectionate or withdrawn, depending on her personality.
- Pinking Up: The nipples become more prominent and pink.
- Abdominal Enlargement: Her belly will start to grow as the kittens develop.
- Decreased Activity: The queen may become less active and prefer resting.
Nutritional Needs During Pregnancy
Proper nutrition is critical for a healthy pregnancy. A pregnant cat requires a diet high in protein and calories to support fetal development and her own health. Here are some key nutritional considerations:
- High-Quality Protein: Ensure the diet contains at least 30% protein.
- Fat Content: Include healthy fats to support fetal growth.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Provide essential vitamins like folic acid and minerals like calcium.
- Hydration: Encourage water intake to prevent dehydration.
Common Health Issues During Pregnancy
While most pregnancies proceed smoothly, some queens may experience health issues. These include:
- Pseudopregnancy: A condition where the queen exhibits signs of pregnancy without actually being pregnant.
- Toxemia: A rare but serious condition that can occur in late pregnancy, characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can pose risks to both the queen and her kittens.
Regular veterinary check-ups can help identify and address these issues early.
Preparing for Labor and Delivery
Creating a Nesting Box
Provide your cat with a comfortable and safe space to give birth. A nesting box should be:
- Clean and spacious
- Located in a quiet, low-traffic area
- Lined with soft bedding
Monitoring for Signs of Labor
As labor approaches, monitor your cat for signs such as:
- Restlessness and nesting behavior
- Decreased appetite
- Temperature drop (normal body temperature is around 101°F)
Labor and Delivery Process
Delivery typically lasts several hours, with each kitten being born every 30-60 minutes. The queen will lick the kittens to stimulate breathing and sever the umbilical cord. It’s important to stay nearby but avoid interfering unless complications arise. If the queen shows signs of distress or the delivery takes too long, contact your veterinarian immediately.
Postpartum Care for Mother and Kittens
Caring for the Mother
After delivery, the queen will need rest and proper nutrition. Continue providing a high-quality diet and ensure she has access to fresh water. Monitor her for any signs of infection or complications, such as fever or unusual discharge.
Caring for the Kittens
The kittens are entirely dependent on their mother for the first few weeks. Ensure they are warm, well-fed, and gaining weight. Regular veterinary check-ups are recommended to monitor their development and address any concerns.
Importance of Spaying Cats
Spaying your cat can prevent unwanted pregnancies and reduce the risk of certain health issues, such as uterine infections and mammary cancer. If you do not plan to breed your cat, consider spaying her after consulting with your veterinarian. This responsible action helps control the feline population and ensures your cat’s long-term health.
Conclusion
Understanding the pregnancy cycle of cats is vital for ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and her kittens. From recognizing the signs of pregnancy to providing proper care during each stage, this guide has covered all the essential aspects of feline gestation. Remember to consult your veterinarian for personalized advice and support throughout the process.
We invite you to share your experiences or ask questions in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into pet care and wellness. Together, let’s create a better world for our feline companions!
Data Source: VCA Hospitals, Merck Veterinary Manual.